Q: What does a “Connected Communities” project in Murfreesboro, TN have in common with NYSERDA’s new “Intelligent Buildings” funding opportunity and Lawrence Berkeley National Lab’s Open Building Operating System?
A: They all seek to leverage interoperable and open-source technologies to enable and support advanced demand management by cost-effective orchestration of diverse energy assets in buildings.
In this post, ACE IoT highlights three seemingly disparate announcements and a notable common thread that connects them. We also consider whether 2023 might be the start of a new era of demand flexibility (DF) in buildings.
Residential Demand Response Through Connected MHA
In July 2023, the first residents of a new multi-family development constructed by the Murfreesboro Housing Authority (MHA) started their move-in. The move-in coincided with the launch of an innovative Connected Communities Project designed to explore the benefits of using advanced connectivity and control to facilitate smarter energy management via a partnership between MHA, SmartMark Communications, Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Middle Tennessee Electric (MTE), ACE IoT Solutions and the Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA). Participating residents give permission to MTE to adjust thermostats and water heaters during a limited number of dates/times when the utility anticipates demand for electricity will reach a peak level.
To manage their participation in the program, residents use the Open HEMS mobile app, developed as part of a separate Connected Communities Initiative and customized for MTE’s customers to communicate with connected thermostats and water heaters. This Open HEMS mobile app is built upon DOE BTO’s VOLTTRON platform. Residents receive a $15 monthly incentive for their participation in the project.
For MTE and TVA, the pilot project provides an opportunity to evaluate an advanced demand management solution that leverages open-source technologies. Threshold research questions include:
Can the solution meaningfully reduce the energy demands of multi-family residential customers during anticipated energy demand peaks?
Using models and optimizations developed and tested by researchers from Oak Ridge National Lab (ORNL), can advanced demand management solutions reduce energy demands without impacting resident comfort?
To what extent do demand management solutions, like the one deployed at the new MHA multi-family development, help deliver grid services–designed to provide value to both utilities and communities via reduced GHG emissions and through avoided electricity generation and/or delivery costs?
Looking ahead: In 2024, the project team expects to release research findings, programmatic best practices, technological documentation, and open-source code that will allow utilities, real estate developers, housing authorities, and other forward-looking organizations to replicate a similar advanced demand management project in their communities.
NYSERDA Intelligent Buildings Program Opportunity Notice (PON)
On July 28, 2023, NYSERDA announced an $18M NextGen Buildings Innovation Challenge, including newly available funding for advanced intelligent building control solutions. NYSERDA highlights the following examples of intelligent building technologies: automated system optimization (ASO) for building automation systems (BAS), smart electrical panels, home energy management systems (HEMS), smart thermostats, connected water heaters, and smart electric vehicle (EV) chargers.
Based on NYSERDA’s calculations, intelligent buildings technologies could save New York state approximately $500M in power system costs and cut 3 million tons of carbon dioxide equivalent annually by 2030. Included in NYSERDA’s calculation of the value of intelligent buildings technologies is “reduced energy consumption and peak demand, monetary compensation from providing a grid resource such as load flexibility, health and economic benefits to occupants, building operational efficiency, resiliency.” Here, the newly released NYSERDA PON reads like an endorsement of advanced demand management solutions like the one being deployed in Murfreesboro, Tennessee.
To NYSERDA, it is problematic that intelligent building technologies “focus on optimizing one building asset, tend to focus on large commercial buildings (e.g. fault detection diagnostics) or single-family homes (e.g. smart thermostat), and tend to be siloed through manufacturer proprietary controls.” The funding that NYSERDA has made available in July 2023 seeks to address the low penetration of intelligent building management controls by funding “new technologies to fully integrate between and control across multiple energy assets to realize the full potential from the stacked value of coordinating these assets.”
The importance of “Interoperability and reliable communication between energy assets” via cloud application programming interface (API)s and grid-edge communication receives a special acknowledgement in NYSERDA’s PON. As does the fact that a building should be able to continue self-managing even when a cloud connection or API service goes down. Notably, these are both central features of the advanced demand management solution deployed in Murfreesboro, TN.
Looking ahead: The application deadline is September 27, 2023. According to information presented during a pre-application webinar, NYSERDA aims to select and fund projects before the start of 2024.
Open Building Operating System (OpenBOS): an Open-Source Grid Responsive Control Platform for Buildings
With support from the New York State Energy Research & Development Authority (NYSERDA), researchers at Lawrence Berkeley National Lab (LBNL) conducted demonstration deployment of an Open Building Operating System (OpenBOS) in March 2023.
In the demonstration deployment, the OpenBOS reduced electricity costs at the site by 27%, demand during a shed event by 49%, and furnace usage by 35%. An overview of the project has been published to the Lawrence Berkeley National Lab website.
According to researchers at LBNL, OpenBOS provides “a scalable method for deploying control applications in small and medium sized buildings.” The solution leverages the open-source VOLTTRON technology to connect applications, equipment and energy assets in the building and external data sources and orchestrate the required read/write commands. OpenBOS also leverages semantic models to enable the development of applications that can be portable across buildings and over the whole life cycle of an individual building. In the demonstration project in New York, the LBNL researchers deployed a Demand Flexibility (DF) control application that can be “easily configured” using a semantic model. See a tech diagram of Open BOS copied below.
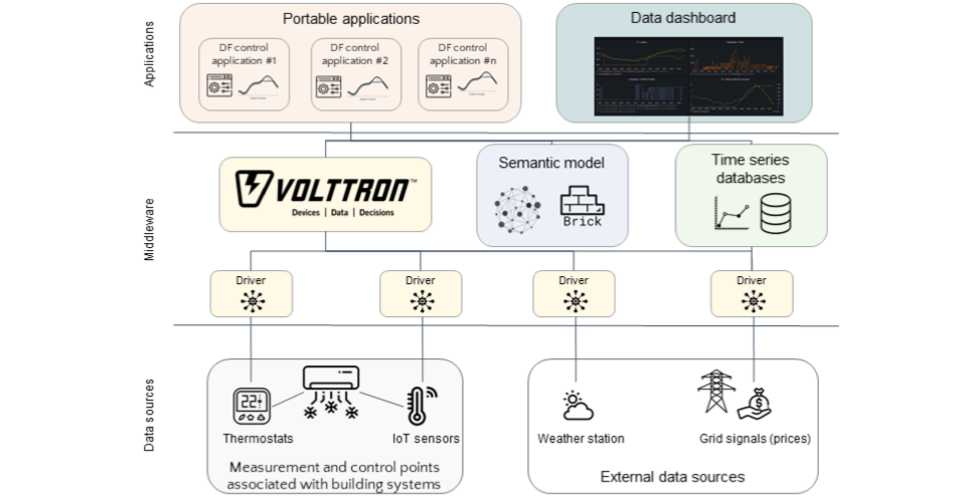
Since OpenBOS was developed to be a cost-effective and replicable solution for small and medium buildings, it is not a coincidence that the architecture of OpenBOS is consistent with both the Connected Communities project in Murfreesboro and with the guidelines included in the NYSERDA Intelligent Buildings PON.
**Looking ahead: **All OpenBOS’s components are open-source and completely free to use and can be easily replicated at other buildings.
A New Era for Demand Response?
The commonality between pilot in Murfreesboro, the Intelligent Buildings funding released by NYSREDA, LBNL’s release of Open BOS Demand signals a transition from Demand Response (DR) to Demand Flexibility (DF). A September 2022 report issued by the National Association of State Energy Officials (NASEO) rightly highlights a DR-DF continuum, “progressing from traditional one-way DR through automated DR of smart, efficient equipment and appliances to highly dynamic, flexible, and interactive management of multiple DERs in real time.”
It is premature to announce a new era for DR—one-way DR initiatives will, no doubt, continue to deliver important value to utilities, the power grid and communities for years to come. Nonetheless, from ACE IoT’s perspective, there has been an unmistakable acceleration along the DR continuum toward Demand Flexibility in 2023. More and more of the building blocks needed for a replicable and scalable deployment Demand Flexibility control technologies are available. This is a very exciting development.
Please follow ACE IoT on LinkedIN.